Model for Bayesian Network
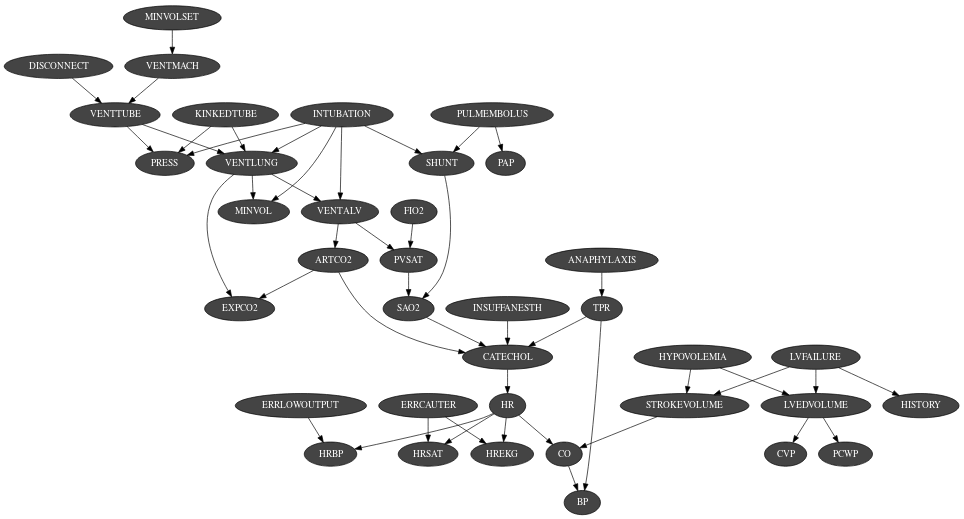
The Bayesian network is the main graphical model of pyagrum. A Bayesian network is a directed probabilistic graphical model based on a DAG. It represents a joint distribution over a set of random variables. In pyAgrum, the variables are (for now) only discrete.
A Bayesian network uses a directed acyclic graph (DAG) to represent conditional independence in the joint distribution. These conditional independence allow to factorize the joint distribution, thereby allowing to compactly represent very large ones.
Moreover, inference algorithms can also use this graph to speed up the computations. Finally, the Bayesian networks can be learnt from data.
class pyagrum.BayesNet(*args)
Section titled “class pyagrum.BayesNet(*args)”BayesNet represents a Bayesian network.
BayesNet(name=’’) -> BayesNet : Parameters: : - name (str) – the name of the Bayes Net
BayesNet(source) -> BayesNet : Parameters: : - source (pyagrum.BayesNet) – the Bayesian network to copy
add(*args)
Section titled “add(*args)”Add a variable to the pyagrum.BayesNet.
- Parameters:
- variable (pyagrum.DiscreteVariable) – the variable added
- descr (str) – the description of the variable (following fast syntax)
- nbrmod (int) – the number of modalities for the new variable
- id (int) – the variable forced id in the pyagrum.BayesNet
- Returns: the id of the new node
- Return type: int
- Raises:
- pyagrum.DuplicateLabel – If variable.name() or id is already used in this pyagrum.BayesNet.
- pyagrum.NotAllowed – If nbrmod is less than 2
addAMPLITUDE(var)
Section titled “addAMPLITUDE(var)”Others aggregators
- Parameters:
- variable (pyagrum.DiscreteVariable) – the variable to be added
- var (
DiscreteVariable)
- Returns: the id of the added value
- Return type: int
addAND(var)
Section titled “addAND(var)”Add a variable, it’s associate node and an AND implementation.
The id of the new variable is automatically generated.
- Parameters:
- variable (pyagrum.DiscreteVariable) – The variable added by copy.
- var (
DiscreteVariable)
- Returns: the id of the added variable.
- Return type: int
- Raises: pyagrum.SizeError – If variable.domainSize()>2
addArc(*args)
Section titled “addArc(*args)”Add an arc in the BN, and update arc.head’s CPT.
- Parameters:
- head (Union [**int ,**str ]) – a variable’s id (int) or name
- head – a variable’s id (int) or name
- Raises:
- pyagrum.InvalidEdge – If arc.tail and/or arc.head are not in the BN.
- pyagrum.DuplicateElement – If the arc already exists.
- Return type:
None
addArcs(listArcs)
Section titled “addArcs(listArcs)”add a list of arcs in te model.
- Parameters: listArcs (List [**Tuple [**intstr ,**intstr ] ]) – the list of arcs
addCOUNT(var, value=1)
Section titled “addCOUNT(var, value=1)”Others aggregators
- Parameters:
- variable (pyagrum.DiscreteVariable) – the variable to be added
- var (
DiscreteVariable) - value (
int)
- Returns: the id of the added value
- Return type: int
addEXISTS(var, value=1)
Section titled “addEXISTS(var, value=1)”Others aggregators
- Parameters:
- variable (pyagrum.DiscreteVariable) – the variable to be added
- var (
DiscreteVariable) - value (
int)
- Returns: the id of the added value
- Return type: int
addFORALL(var, value=1)
Section titled “addFORALL(var, value=1)”Others aggregators
- Parameters:
- variable (pyagrum.DiscreteVariable) – the variable to be added
- var (
DiscreteVariable) - value (
int)
- Returns: the id of the added variable.
- Return type: int
addLogit(*args)
Section titled “addLogit(*args)”Add a variable, its associate node and a Logit implementation.
(The id of the new variable can be automatically generated.)
- Parameters:
- variable (pyagrum.DiscreteVariable) – The variable added by copy
- externalWeight (float) – the added external weight
- id (int) – The proposed id for the variable.
- Returns: the id of the added variable.
- Return type: int
- Raises: pyagrum.DuplicateElement – If id is already used
addMAX(var)
Section titled “addMAX(var)”Others aggregators
- Parameters:
- variable (pyagrum.DiscreteVariable) – the variable to be added
- var (
DiscreteVariable)
- Returns: the id of the added value
- Return type: int
addMEDIAN(var)
Section titled “addMEDIAN(var)”Others aggregators
- Parameters:
- variable (pyagrum.DiscreteVariable) – the variable to be added
- var (
DiscreteVariable)
- Returns: the id of the added value
- Return type: int
addMIN(var)
Section titled “addMIN(var)”Others aggregators
- Parameters:
- variable (pyagrum.DiscreteVariable) – the variable to be added
- var (
DiscreteVariable)
- Returns: the id of the added value
- Return type: int
addNoisyAND(*args)
Section titled “addNoisyAND(*args)”Add a variable, its associate node and a noisyAND implementation.
(The id of the new variable can be automatically generated.)
- Parameters:
- variable (pyagrum.DiscreteVariable) – The variable added by copy
- externalWeight (float) – the added external weight
- id (int) – The proposed id for the variable.
- Returns: the id of the added variable.
- Return type: int
- Raises: pyagrum.DuplicateElement – If id is already used
addNoisyOR(*args)
Section titled “addNoisyOR(*args)”Add a variable, it’s associate node and a noisyOR implementation.
Since it seems that the ‘classical’ noisyOR is the Compound noisyOR, we keep the addNoisyOR as an alias for addNoisyORCompound.
(The id of the new variable can be automatically generated.)
- Parameters:
- variable (pyagrum.DiscreteVariable) – The variable added by copy
- externalWeight (float) – the added external weight
- id (int) – The proposed id for the variable.
- Returns: the id of the added variable.
- Return type: int
- Raises: pyagrum.DuplicateElement – If id is already used
addNoisyORCompound(*args)
Section titled “addNoisyORCompound(*args)”Add a variable, it’s associate node and a noisyOR implementation.
Since it seems that the ‘classical’ noisyOR is the Compound noisyOR, we keep the addNoisyOR as an alias for addNoisyORCompound.
(The id of the new variable can be automatically generated.)
- Parameters:
- variable (pyagrum.DiscreteVariable) – The variable added by copy
- externalWeight (float) – the added external weight
- id (int) – The proposed id for the variable.
- Returns: the id of the added variable.
- Return type: int
- Raises: pyagrum.DuplicateElement – If id is already used
addNoisyORNet(*args)
Section titled “addNoisyORNet(*args)”Add a variable, its associate node and a noisyOR implementation.
Since it seems that the ‘classical’ noisyOR is the Compound noisyOR, we keep the addNoisyOR as an alias for addNoisyORCompound.
(The id of the new variable can be automatically generated.)
- Parameters:
- variable (pyagrum.DiscreteVariable) – The variable added by copy
- externalWeight (float) – the added external weight
- id (int) – The proposed id for the variable.
- Returns: the id of the added variable.
- Return type: int
addOR(var)
Section titled “addOR(var)”Add a variable, it’s associate node and an OR implementation.
The id of the new variable is automatically generated.
Warning
If parents are not boolean, all value>1 is True
- Parameters:
- variable (pyagrum.DiscreteVariable) – The variable added by copy
- var (
DiscreteVariable)
- Returns: the id of the added variable.
- Return type: int
- Raises: pyagrum.SizeError – If variable.domainSize()>2
addSUM(var)
Section titled “addSUM(var)”Others aggregators
- Parameters:
- variable (pyagrum.DiscreteVariable) – the variable to be added
- var (
DiscreteVariable)
- Returns: the id of the added value
- Return type: int
addStructureListener(whenNodeAdded=None, whenNodeDeleted=None, whenArcAdded=None, whenArcDeleted=None)
Section titled “addStructureListener(whenNodeAdded=None, whenNodeDeleted=None, whenArcAdded=None, whenArcDeleted=None)”Add the listeners in parameters to the list of existing ones.
- Parameters:
- whenNodeAdded (lambda expression) – a function for when a node is added
- whenNodeDeleted (lambda expression) – a function for when a node is removed
- whenArcAdded (lambda expression) – a function for when an arc is added
- whenArcDeleted (lambda expression) – a function for when an arc is removed
addVariables(listFastVariables, default_nbr_mod=2)
Section titled “addVariables(listFastVariables, default_nbr_mod=2)”Add a list of variable in the form of ‘fast’ syntax.
- Parameters:
- listFastVariables (List [**str ]) – the list of variables in ‘fast’ syntax.
- default_nbr_mod (int) – the number of modalities for the variable if not specified following fast syntax. Note that default_nbr_mod=1 is mandatory to create variables with only one modality (for utility for instance).
- Returns: the list of created ids.
- Return type: List[int]
addWeightedArc(*args)
Section titled “addWeightedArc(*args)”Add an arc in the BN, and update arc.head’s CPT.
- Parameters:
- head (Union [**int ,**str ]) – a variable’s id (int) or name
- tail (Union [**int ,**str ]) – a variable’s id (int) or name
- causalWeight (float) – the added causal weight
- Raises:
- pyagrum.InvalidArc – If arc.tail and/or arc.head are not in the BN.
- pyagrum.InvalidArc – If variable in arc.head is not a NoisyOR variable.
- Return type:
None
adjacencyMatrix()
Section titled “adjacencyMatrix()”adjacency matrix from a graph/graphical models
Compute the adjacency matrix of a pyAgrum’s graph or graphical models (more generally an object that has nodes, children/parents or neighbours methods)
- Returns: adjacency matrix (as numpy.ndarray) with nodeId as key.
- Return type: numpy.ndarray
ancestors(norid)
Section titled “ancestors(norid)”give the set of nodeid of ancestors of a node
- Parameters: norid (str |**int) – the name or the id of the node
- Returns: the set of ids of the ancestors of node norid.
- Return type: Set[int]
arcs()
Section titled “arcs()”- Returns: The lisf of arcs in the IBayesNet
- Return type: list
beginTopologyTransformation()
Section titled “beginTopologyTransformation()”When inserting/removing arcs, node CPTs change their dimension with a cost in time. begin Multiple Change for all CPTs These functions delay the CPTs change to be done just once at the end of a sequence of topology modification, begins a sequence of insertions/deletions of arcs without changing the dimensions of the CPTs.
- Return type:
None
changeTensor(*args)
Section titled “changeTensor(*args)”change the CPT associated to nodeId to newPot delete the old CPT associated to nodeId.
- Parameters:
- var (Union [**int ,**str ]) – the current name or the id of the variable
- newPot (pyagrum.Tensor) – the new tensor
- Raises: pyagrum.NotAllowed – If newPot has not the same signature as __probaMap[NodeId]
- Return type:
None
changeVariableLabel(*args)
Section titled “changeVariableLabel(*args)”change the label of the variable associated to nodeId to the new value.
- Parameters:
- var (Union [**int ,**str ]) – the current name or the id of the variable
- old_label (str) – the new label
- new_label (str) – the new label
- Raises: pyagrum.NotFound – if id/name is not a variable or if old_label does not exist.
- Return type:
None
changeVariableName(*args)
Section titled “changeVariableName(*args)”Changes a variable’s name in the “pyagrum.BayesNet”.
This will change the “pyagrum.DiscreteVariable” names in the “pyagrum.BayesNet”.
- Parameters:
- var (Union [**int ,**str ]) – the current name or the id of the variable
- new_name (str) – the new name of the variable
- Raises:
- pyagrum.DuplicateLabel – If new_name is already used in this BayesNet.
- pyagrum.NotFound – If no variable matches id.
- Return type:
None
check()
Section titled “check()”Check if the BayesNet is consistent (variables, CPT, …)
- Returns: list of found issues
- Return type: List[str]
children(norid)
Section titled “children(norid)”- Parameters:
- id (int) – the id of the parent
- norid (
object)
- Returns: the set of all the children
- Return type: Set
clear()
Section titled “clear()”Clear the whole BayesNet
- Return type:
None
completeInstantiation()
Section titled “completeInstantiation()”Give an instantiation over all the variables of the model
- Returns: a complete Instantiation for the model
- Return type: pyagrum.Instantiation
connectedComponents()
Section titled “connectedComponents()”connected components from a graph/graphical models
Compute the connected components of a pyAgrum’s graph or graphical models (more generally an object that has nodes, children/parents or neighbours methods)
The firstly visited node for each component is called a ‘root’ and is used as a key for the component. This root has been arbitrarily chosen during the algorithm.
- Returns: dict of connected components (as set of nodeIds (int)) with a nodeId (root) of each component as key.
- Return type: dict(int,Set[int])
contextualize(*args)
Section titled “contextualize(*args)”- Return type:
BayesNet
cpt(*args)
Section titled “cpt(*args)”Returns the CPT of a variable.
- Parameters: VarId (Union [**int ,**str ]) – a variable’s id (int) or name
- Returns: The variable’s CPT.
- Return type: pyagrum.Tensor
- Raises: pyagrum.NotFound – If no variable’s id matches varId.
- Returns: a constant reference to the dag of this BayesNet.
- Return type: pyagrum.DAG
descendants(norid)
Section titled “descendants(norid)”give the set of nodeid of descendants of a node
- Parameters: norid (str |**int) – the name or the id of the node
- Returns: the set of ids of the descendants of node norid.
- Return type: Set[int]
Returns the dimension (the number of free parameters) in this BayesNet.
- Returns: the dimension of the BayesNet
- Return type: int
empty()
Section titled “empty()”Check if there are some variables in the model.
- Returns: True if there is no variable in the model.
- Return type: bool
endTopologyTransformation()
Section titled “endTopologyTransformation()”Terminates a sequence of insertions/deletions of arcs by adjusting all CPTs dimensions. End Multiple Change for all CPTs.
- Return type: pyagrum.BayesNet
erase(*args)
Section titled “erase(*args)”Remove a variable from the “pyagrum.BayesNet”.
Removes the corresponding variable from the “pyagrum.BayesNet” and from all of it’s children “pyagrum.Tensor”.
If no variable matches the given id, then nothing is done.
- Parameters: var (Union [**int ,**str ,pyagrum.DiscreteVariable ]) – the current name, the id of the variable or a reference to the variable
- Return type:
None
eraseArc(*args)
Section titled “eraseArc(*args)”Removes an arc in the BN, and update head’s CTP.
If (tail, head) doesn’t exist, the nothing happens.
- Parameters:
- arc (pyagrum.Arc when calling eraseArc (**arc )) – The arc to be removed.
- head (Union [**int ,**str ]) – a variable’s id (int) or name for the head when calling eraseArc(head,tail)
- tail (Union [**int ,**str ]) – a variable’s id (int) or name for the tail when calling eraseArc(head,tail)
- Return type:
None
evEq(name, value)
Section titled “evEq(name, value)”This method is used to set an observation on a quasi-continuous variables (pyagrum .DiscretizedVariable with a large number of ticks) that the variable is equal to a given value.
Note
- see also
Tensor.evEq() - see also
BayesNet.evGt(),BayesNet.evLt(),BayesNet.evIn()
Examples
>>> import pyagrum as gum>>> bn = pyagrum.fastBN('A[0:10:20]'') # DiscretizedVariable from 0 to 10 in 20 steps>>> print(bn.evEqu('A',5) A |[0;0.5[ |[0.5;1[ |[1;1.5[ |[1.5;2[ |[2;2.5[ |[2.5;3[ |[3;3.5[ |[3.5;4[ |[4;4.5[ |[4.5;5[ |[5;5.5[ |[5.5;6[ |[6;6.5[ |[6.5;7[ |[7;7.5[ |[7.5;8[ |[8;8.5[ |[8.5;9[ |[9;9.5[ |[9.5;10] |---------|---------|---------|---------|---------|---------|---------|---------|---------|---------|---------|---------|---------|---------|---------|---------|---------|---------|---------|---------| 0.0000 | 0.0000 | 0.0000 | 0.0000 | 0.0000 | 0.0000 | 0.0000 | 0.0000 | 0.0000 | 0.0000 | 1.0000 | 0.0000 | 0.0000 | 0.0000 | 0.0000 | 0.0000 | 0.0000 | 0.0000 | 0.0000 | 0.0000 |- Parameters:
- var (Union [**int ,**str ]) – the current name or the id of the variable
- value (float)
- name (
str)
- Returns:
The representation of the evidence as a
Tensor. - Return type: pyAgrum.Tensor
evGt(name, value)
Section titled “evGt(name, value)”This method is used to set an obvervation on a quasi-continuous variables (pyagrum .DiscretizedVariable with a large number of ticks) that the variable greater than a given value.
Note
- see also
Tensor.evGt() - see also
BayesNet.evEq(),BayesNet.evLt(),BayesNet.evIn()
Examples
>>> import pyagrum as gum>>> bn = pyagrum.fastBN('A[0:10:20]'') # DiscretizedVariable from 0 to 10 in 20 steps>>> print(bn.eGt('A',5) A |[0;0.5[ |[0.5;1[ |[1;1.5[ |[1.5;2[ |[2;2.5[ |[2.5;3[ |[3;3.5[ |[3.5;4[ |[4;4.5[ |[4.5;5[ |[5;5.5[ |[5.5;6[ |[6;6.5[ |[6.5;7[ |[7;7.5[ |[7.5;8[ |[8;8.5[ |[8.5;9[ |[9;9.5[ |[9.5;10] |---------|---------|---------|---------|---------|---------|---------|---------|---------|---------|---------|---------|---------|---------|---------|---------|---------|---------|---------|---------| 0.0000 | 0.0000 | 0.0000 | 0.0000 | 0.0000 | 0.0000 | 0.0000 | 0.0000 | 0.0000 | 0.0000 | 1.0000 | 1.0000 | 1.0000 | 1.0000 | 1.0000 | 1.0000 | 1.0000 | 1.0000 | 1.0000 | 1.0000 |- Parameters:
- var (Union [**int ,**str ]) – the current name or the id of the variable
- value (float)
- name (
str)
- Returns:
The representation of the evidence as a
Tensor. - Return type: pyAgrum.Tensor
evIn(name, val1, val2)
Section titled “evIn(name, val1, val2)”This method is used to set an obvervation on a quasi-continuous variables (pyagrum .DiscretizedVariable with a large number of ticks) that the variable is less than a given value.
Note
- see also
Tensor.evIn() - see also
BayesNet.evEq(),BayesNet.evGt(),BayesNet.evLt()
- Parameters:
- var (Union [**int ,**str ]) – the current name or the id of the variable
- valueMin (float) – the minimum value
- valueMax (float) – the maximum value
- name (
str) - val1 (
float) - val2 (
float)
- Returns:
The representation of the evidence as a
Tensor. - Return type: pyagrum.Tensor
evLt(name, value)
Section titled “evLt(name, value)”This method is used to set an obvervation on a quasi-continuous variables (pyagrum .DiscretizedVariable with a large number of ticks) that the variable is less than a given value.
Note
- see also
Tensor.evLt() - see also
BayesNet.evEq(),BayesNet.evGt(),BayesNet.evIn()
- Parameters:
- var (Union [**int ,**str ]) – the current name or the id of the variable
- value (float)
- name (
str)
- Returns:
The representation of the evidence as a
Tensor. - Return type: pyAgrum.Tensor
exists(*args)
Section titled “exists(*args)”Check if a node with this name or id exists
- Parameters: norid (str |**int) – name or id of the searched node
- Returns: True if there is a node with such a name or id
- Return type: bool
existsArc(*args)
Section titled “existsArc(*args)”Check if an arc exists
- Parameters:
- tail (str |**int) – the name or id of the tail of the arc
- head (str |**int) – the name or the id of the head of the arc
- Returns: True if tail->head is an arc.
- Return type: bool
family(norid)
Section titled “family(norid)”give the set of parents of a node and the node
- Parameters: norid (str |**int) – the node
- Returns: the set of nodeId of the family of the node norid
- Return type: Set[int]
static fastPrototype(*args)
Section titled “static fastPrototype(*args)”Create a Bayesian network with a dot-like syntax which specifies: : - the structure ‘a->b->c;b->d<-e;’.
- the type of the variables with different syntax:
- by default, a variable is a binary pyagrum.RangeVariable using the default domain size ([2])
- with ‘a[10]’, the variable is a pyagrum.RangeVariable using 10 as domain size (from 0 to 9)
- with ‘a[3,7]’, the variable is a pyagrum.RangeVariable using a domainSize from 3 to 7
- with ‘a[1,3.14,5,6.2]’, the variable is a pyagrum.DiscretizedVariable using the given ticks (at least 3 values)
- with ‘a[0.0:3.14:10]’, the variable is a pyagrum.DiscretizedVariable of 10 intervals of same width from 0 to 3.14 (including both)
- with ‘a{top|middle|bottom}’, the variable is a pyagrum.LabelizedVariable using the given labels.
- with ‘a{-1|5|0|3}’, the variable is a pyagrum.IntegerVariable using the sorted given values.
- with ‘a{-0.5|5.01|0|3.1415}’, the variable is a pyagrum.NumericalDiscreteVariable using the sorted given values.
Note
- If the dot-like string contains such a specification more than once for a variable, the first specification will be used.
- the CPTs are randomly generated.
- see also the function pyagrum.fastBN.
Examples
>>> import pyagrum as gum>>> bn=pyagrum.BayesNet.fastPrototype('A->B[1,3]<-C{yes|No}->D[2,4]<-E[1,2.5,3.9]',6)- Parameters:
- dotlike (str) – the string containing the specification
- domainSize (int or str) – the default domain size or the default domain for variables
- Returns: the resulting Bayesian network
- Return type: pyagrum.BayesNet
generateCPT(*args)
Section titled “generateCPT(*args)”Randomly generate CPT for a given node in a given structure.
- Parameters: node (Union [**int ,**str ]) – a variable’s id (int) or name
- Return type:
None
generateCPTs()
Section titled “generateCPTs()”Randomly generates CPTs for a given structure.
- Return type:
None
hasSameStructure(other)
Section titled “hasSameStructure(other)”- Parameters: pyagrum.DAGmodel – a direct acyclic model
- Returns: True if all the named node are the same and all the named arcs are the same
- Return type: bool
idFromName(name)
Section titled “idFromName(name)”Returns a variable’s id given its name in the graph.
- Parameters: name (str) – The variable’s name from which the id is returned.
Notes
A convenient shortcut for g.variableFromName(name) is g[name].
- Returns: The variable’s node id.
- Return type: int
- Raises: pyagrum.NotFound – If name does not match a variable in the graph
ids(names)
Section titled “ids(names)”List of ids for a list of names of variables in the model
- Parameters:
- lov (List [**str ]) – List of variable names
- names (
list[str])
- Returns: The ids for the list of names of the graph variables
- Return type: List[int]
isIndependent(*args)
Section titled “isIndependent(*args)”check if nodes X and nodes Y are independent given nodes Z
- Parameters:
- X (str |**intList [**str |**int ]) – a list of of nodeIds or names
- Y (str |**intList [**str |**int ]) – a list of of nodeIds or names
- Z (str |**intList [**str |**int ]) – a list of of nodeIds or names
- Raises: InvalidArgument – if X and Y share variables
- Returns: True if X and Y are independent given Z in the model
- Return type: bool
jointProbability(i)
Section titled “jointProbability(i)”- Parameters: i (pyagrum.instantiation) – an instantiation of the variables
- Returns: a parameter of the joint probability for the BayesNet
- Return type: float
Warning
a variable not present in the instantiation is assumed to be instantiated to 0
loadBIF(name, l=None)
Section titled “loadBIF(name, l=None)”Load a BIF file.
- Parameters:
- name (str) – the file’s name
- l (list) – list of functions to execute
- Raises:
- pyagrum.IOError – If file not found
- pyagrum.FatalError – If file is not valid
- Return type:
str
loadBIFXML(name, l=None)
Section titled “loadBIFXML(name, l=None)”Load a BIFXML file.
- Parameters:
- name (str) – the name’s file
- l (list) – list of functions to execute
- Raises:
- pyagrum.IOError – If file not found
- pyagrum.FatalError – If file is not valid
- Return type:
str
loadDSL(name, l=None)
Section titled “loadDSL(name, l=None)”Load a DSL file.
- Parameters:
- name (str) – the file’s name
- l (list) – list of functions to execute
- Raises:
- pyagrum.IOError – If file not found
- pyagrum.FatalError – If file is not valid
- Return type:
str
loadNET(name, l=None)
Section titled “loadNET(name, l=None)”Load a NET file.
- Parameters:
- name (str) – the name’s file
- l (list) – list of functions to execute
- Raises:
- pyagrum.IOError – If file not found
- pyagrum.FatalError – If file is not valid
- Return type:
str
loadO3PRM(*args)
Section titled “loadO3PRM(*args)”Load an O3PRM file.
Warning
The O3PRM language is the only language allowing to manipulate not only DiscretizedVariable but also RangeVariable and LabelizedVariable.
- Parameters:
- name (str) – the file’s name
- system (str) – the system’s name
- classpath (str) – the classpath
- l (list) – list of functions to execute
- Raises:
- pyagrum.IOError – If file not found
- pyagrum.FatalError – If file is not valid
- Return type:
str
loadUAI(name, l=None)
Section titled “loadUAI(name, l=None)”Load an UAI file.
- Parameters:
- name (str) – the name’s file
- l (list) – list of functions to execute
- Raises:
- pyagrum.IOError – If file not found
- pyagrum.FatalError – If file is not valid
- Return type:
str
loadXDSL(name, l=None)
Section titled “loadXDSL(name, l=None)”Load a XDSL file.
- Parameters:
- name (str) – the file’s name
- l (list) – list of functions to execute
- Raises:
- pyagrum.IOError – If file not found
- pyagrum.FatalError – If file is not valid
- Return type:
str
log10DomainSize()
Section titled “log10DomainSize()”returns the log10 of the domain size of the model defined as the product of the domain sizes of the variables in the model.
- Returns: the log10 domain size.
- Return type: float
log2JointProbability(i)
Section titled “log2JointProbability(i)”- Parameters: i (pyagrum.instantiation) – an instantiation of the variables
- Returns: a parameter of the log joint probability for the BayesNet
- Return type: float
Warning
a variable not present in the instantiation is assumed to be instantiated to 0
maxNonOneParam()
Section titled “maxNonOneParam()”- Returns: The biggest value (not equal to 1) in the CPTs of the BayesNet
- Return type: float
maxParam()
Section titled “maxParam()”- Returns: the biggest value in the CPTs of the BayesNet
- Return type: float
maxVarDomainSize()
Section titled “maxVarDomainSize()”- Returns: the biggest domain size among the variables of the BayesNet
- Return type: int
memoryFootprint()
Section titled “memoryFootprint()”get the size (in byte) of the (main footprint) of the BayesNet
- Returns: the size in byte of the representation (of the parameters) of the BayesNet
- Return type: int
minNonZeroParam()
Section titled “minNonZeroParam()”- Returns: the smallest value (not equal to 0) in the CPTs of the IBayesNet
- Return type: float
minParam()
Section titled “minParam()”- Returns: the smallest value in the CPTs of the IBayesNet
- Return type: float
minimalCondSet(*args)
Section titled “minimalCondSet(*args)”Returns, given one or many targets and a list of variables, the minimal set of those needed to calculate the target/targets.
- Parameters:
- target (int) – The id of the target
- targets (List [**int ]) – The ids of the targets
- list (List [**int ]) – The list of available variables
- Returns: The minimal set of variables
- Return type: Set[int]
moralGraph()
Section titled “moralGraph()”Returns the moral graph of the BayesNet, formed by adding edges between all pairs of nodes that have a common child, and then making all edges in the graph undirected.
- Returns: The moral graph
- Return type: pyagrum.UndiGraph
moralizedAncestralGraph(nodes)
Section titled “moralizedAncestralGraph(nodes)”build a UndiGraph by moralizing the Ancestral Graph of a list of nodes
- Parameters: nodes (str |**intList [**str |**int ]) – the list of of nodeIds or names
Warning
pyagrum.UndiGraph only knows NodeId. Hence the moralized ancestral graph does not include the names of the variables.graph
- Returns: the moralized ancestral graph of the nodes
- Return type: pyagrum.UndiGraph
names()
Section titled “names()”Set of names of variables in the model
- Returns: The names of the graph variables
- Return type: Set[str]
nodeId(var)
Section titled “nodeId(var)”- Parameters: var (pyagrum.DiscreteVariable) – a variable
- Returns: the id of the variable
- Return type: int
- Raises: pyagrum.IndexError – If the graph does not contain the variable
nodes()
Section titled “nodes()”- Returns: the set of ids
- Return type: Set[int]
nodeset(names)
Section titled “nodeset(names)”Set of ids for a list of names of variables in the model
- Parameters:
- lov (List [**str ]) – List of variable names
- names (
list[str])
- Returns: The set of ids for the list of names of the graph variables
- Return type: Set[int]
parents(norid)
Section titled “parents(norid)”- Parameters:
- id – The id of the child node
- norid (
object)
- Returns: the set of the parents ids.
- Return type: Set
properties()
Section titled “properties()”- Return type:
list[str]
property(name)
Section titled “property(name)”Returns the value associated to this property.
Properties are a way to keep some (name,value) together with de model.
- Parameters: name (str) – the name of the property
- Raises: NotFound – if no name property is found
- Returns: The value associated to this name
- Return type: str
propertyWithDefault(name, byDefault)
Section titled “propertyWithDefault(name, byDefault)”Returns the value associated to this property or the default value if there is no such property.
Properties are a way to keep some information (name,value) together with de model.
- Parameters:
- name (str) – the name of the property
- byDefault (str) – the value by default if no property has been found.
- Returns: The value associated to this name or the value by default.
- Return type: str
reverseArc(*args)
Section titled “reverseArc(*args)”Reverses an arc while preserving the same joint distribution.
- Parameters:
- tail – (int) the id of the tail variable
- head – (int) the id of the head variable
- tail – (str) the name of the tail variable
- head – (str) the name of the head variable
- arc (pyagrum.Arc) – an arc
- Raises: pyagrum.InvalidArc – If the arc does not exsit or if its reversal would induce a directed cycle.
- Return type:
None
saveBIF(name, allowModificationWhenSaving=False)
Section titled “saveBIF(name, allowModificationWhenSaving=False)”Save the BayesNet in a BIF file.
- Parameters:
- name (str) – the file’s name
- allowModificationWhenSaving (bool) – False by default. if true, syntax errors are corrected when saving the file. If false, they throw a FatalError.
- Return type:
None
saveBIFXML(name, allowModificationWhenSaving=False)
Section titled “saveBIFXML(name, allowModificationWhenSaving=False)”Save the BayesNet in a BIFXML file.
- Parameters:
- name (str) – the file’s name
- allowModificationWhenSaving (bool) – False by default. if true, syntax errors are corrected when saving the file. If false, they throw a FatalError.
- Return type:
None
saveDSL(name, allowModificationWhenSaving=False)
Section titled “saveDSL(name, allowModificationWhenSaving=False)”Save the BayesNet in a DSL file.
- Parameters:
- name (str) – the file’s name
- allowModificationWhenSaving (bool) – False by default. if true, syntax errors are corrected when saving the file. If false, they throw a FatalError.
- Return type:
None
saveNET(name, allowModificationWhenSaving=False)
Section titled “saveNET(name, allowModificationWhenSaving=False)”Save the BayesNet in a NET file.
- Parameters:
- name (str) – the file’s name
- allowModificationWhenSaving (bool) – False by default. if true, syntax errors are corrected when saving the file. If false, they throw a FatalError.
- Return type:
None
saveO3PRM(name, allowModificationWhenSaving=False)
Section titled “saveO3PRM(name, allowModificationWhenSaving=False)”Save the BayesNet in an O3PRM file.
Warning
The O3PRM language is the only language allowing to manipulate not only DiscretizedVariable but also RangeVariable and LabelizedVariable.
- Parameters:
- name (str) – the file’s name
- allowModificationWhenSaving (bool) – False by default. if true, syntax errors are corrected when saving the file. If false, they throw a FatalError.
- Return type:
None
saveUAI(name, allowModificationWhenSaving=False)
Section titled “saveUAI(name, allowModificationWhenSaving=False)”Save the BayesNet in an UAI file.
- Parameters:
- name (str) – the file’s name
- allowModificationWhenSaving (bool) – False by default. if true, syntax errors are corrected when saving the file. If false, they throw a FatalError.
- Return type:
None
saveXDSL(name, allowModificationWhenSaving=False)
Section titled “saveXDSL(name, allowModificationWhenSaving=False)”Save the BayesNet in a XDSL file.
- Parameters:
- name (str) – the file’s name
- allowModificationWhenSaving (bool) – (not used). if true, syntax errors are corrected when saving the file. If false, they throw a FatalError.
- Return type:
None
setProperty(name, value)
Section titled “setProperty(name, value)”Create or change the couple (name,value) in the properties.
Properties are a way to keep some information (name,value) together with de model.
- Parameters:
- name (str) – the name of the property
- value (str) – the value of the property.
- Return type:
None
size()
Section titled “size()”- Returns: the number of nodes in the graph
- Return type: int
sizeArcs()
Section titled “sizeArcs()”- Returns: the number of arcs in the graph
- Return type: int
toDot()
Section titled “toDot()”- Returns: a friendly display of the graph in DOT format
- Return type: str
toFast(filename=None)
Section titled “toFast(filename=None)”Export the Bayesian network as fast syntax (in a string or in a python file)
- Parameters: filename (Optional [**str ]) – the name of the file (including the prefix), if None , use sys.stdout
- Return type:
str
topologicalOrder()
Section titled “topologicalOrder()”- Returns: the list of the nodes Ids in a topological order
- Return type: List
- Raises: pyagrum.InvalidDirectedCycle – If this graph contains cycles
variable(*args)
Section titled “variable(*args)”- Parameters:
- id (int) – a variable’s id
- name (str) – a variable’s name
- Returns: the variable
- Return type: pyagrum.DiscreteVariable
- Raises: pyagrum.IndexError – If the graph does not contain the variable
variableFromName(name)
Section titled “variableFromName(name)”- Parameters: name (str) – a variable’s name
- Returns: the variable
- Return type: pyagrum.DiscreteVariable
- Raises: pyagrum.IndexError – If the graph does not contain the variable
variableNodeMap()
Section titled “variableNodeMap()”- Returns: the variable node map
- Return type: pyagrum.variableNodeMap
