Explanation and analysis
This tools aimed to provide some different views on the Bayesian network in order to explore its qualitative and/or quantitave behaviours.
class pyagrum.JunctionTreeGenerator
Section titled “class pyagrum.JunctionTreeGenerator”JunctionTreeGenerator is use to generate junction tree or binary junction tree from Bayesian networks.
JunctionTreeGenerator() -> JunctionTreeGenerator : default constructor
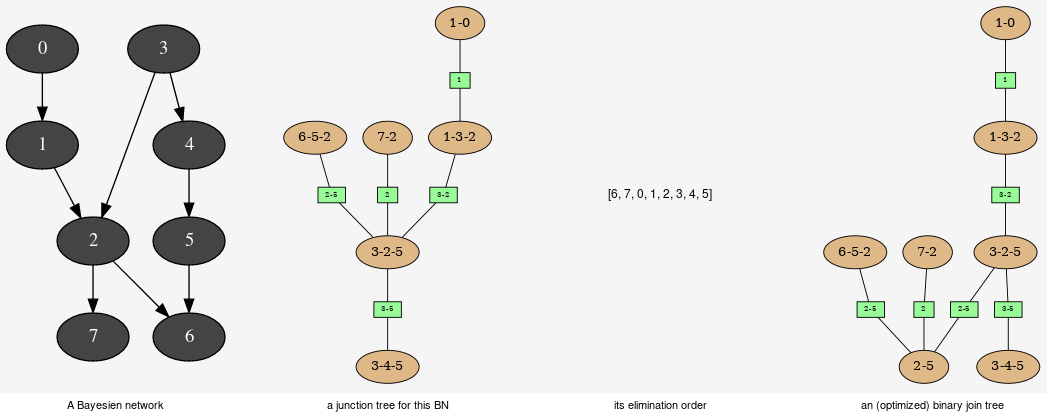
binaryJoinTree(*args)
Section titled “binaryJoinTree(*args)”Computes the binary joint tree for its parameters. If the first parameter is a graph, the heurisitcs assume that all the node have the same domain size (2). If given, the heuristic takes into account the partial order for its elimination order.
- Parameters:
- g (pyagrum.UndiGraph) – a undirected graph
- dag (pyagrum.DAG) – a dag
- bn (pyagrum.BayesNet) – a BayesianNetwork
- partial_order (List [**List [**int ] ]) – a partial order among the nodeIDs
- Returns: the current binary joint tree
- Return type: pyagrum.CliqueGraph
eliminationOrder(*args)
Section titled “eliminationOrder(*args)”Computes the elimination for its parameters. If the first parameter is a graph, the heurisitcs assume that all the node have the same domain size (2). If given, the heuristic takes into account the partial order for its elimination order.
- Parameters:
- g (pyagrum.UndiGraph) – a undirected graph
- dag (pyagrum.DAG) – a dag
- bn (pyagrum.BayesNet) – a BayesianNetwork
- partial_order (List [**List [**int ] ]) – a partial order among the nodeIDs
- Returns: the current elimination order.
- Return type: pyagrum.CliqueGraph
junctionTree(*args)
Section titled “junctionTree(*args)”Computes the junction tree for its parameters. If the first parameter is a graph, the heurisitcs assume that all the node have the same domain size (2). If given, the heuristic takes into account the partial order for its elimination order.
- Parameters:
- g (pyagrum.UndiGraph) – a undirected graph
- dag (pyagrum.DAG) – a dag
- bn (pyagrum.BayesNet) – a BayesianNetwork
- partial_order (List [**List [**int ] ]) – a partial order among the nodeIDs
- Returns: the current junction tree.
- Return type: pyagrum.CliqueGraph
class pyagrum.EssentialGraph(*args)
Section titled “class pyagrum.EssentialGraph(*args)”Class building the essential graph from a BN.
Essential graph is a mixed graph (Chain Graph) that represents the class of markov equivalent Bayesian networks (with the same independency model).
EssentialGraph(m) -> EssentialGraph : Parameters: : - m (pyagrum.DAGmodel) – a DAGmodel
adjacencyMatrix()
Section titled “adjacencyMatrix()”adjacency matrix from a graph/graphical models
Compute the adjacency matrix of a pyAgrum’s graph or graphical models (more generally an object that has nodes, children/parents or neighbours methods)
- Returns: adjacency matrix (as numpy.ndarray) with nodeId as key.
- Return type: numpy.ndarray
arcs()
Section titled “arcs()”- Returns: The lisf of arcs in the EssentialGraph
- Return type: list
children(id)
Section titled “children(id)”- Parameters: id (int) – the id of the parent
- Returns: the set of all the children
- Return type: Set
connectedComponents()
Section titled “connectedComponents()”connected components from a graph/graphical models
Compute the connected components of a pyAgrum’s graph or graphical models (more generally an object that has nodes, children/parents or neighbours methods)
The firstly visited node for each component is called a ‘root’ and is used as a key for the component. This root has been arbitrarily chosen during the algorithm.
- Returns: dict of connected components (as set of nodeIds (int)) with a nodeId (root) of each component as key.
- Return type: dict(int,Set[int])
edges()
Section titled “edges()”- Returns: the list of the edges
- Return type: List
idFromName(name)
Section titled “idFromName(name)”- Parameters: name (str) – the name of the variable in the model
- Returns: the nodeId from the name of the variable in the model
- Return type: int
nameFromId(node)
Section titled “nameFromId(node)”- Parameters: node (int) – the nodeId of the variable in the model
- Returns: the name of the variable in the model from the nodeId
- Return type: str
neighbours(id)
Section titled “neighbours(id)”- Parameters: id (int) – the id of the checked node
- Returns: The set of edges adjacent to the given node
- Return type: Set
nodes()
Section titled “nodes()”- Return type:
object
parents(id)
Section titled “parents(id)”- Parameters:
id (
int) – The id of the child node - Returns: the set of the parents ids.
- Return type: Set
pdag()
Section titled “pdag()”- Returns: the PDAG (Partially Directed Graph)
- Return type: pyagrum.PDAG
size()
Section titled “size()”- Returns: the number of nodes in the graph
- Return type: int
sizeArcs()
Section titled “sizeArcs()”- Returns: the number of arcs in the graph
- Return type: int
sizeEdges()
Section titled “sizeEdges()”- Returns: the number of edges in the graph
- Return type: int
sizeNodes()
Section titled “sizeNodes()”- Returns: the number of nodes in the graph
- Return type: int
skeleton()
Section titled “skeleton()”- Return type:
UndiGraph
toDot()
Section titled “toDot()”- Returns: a friendly display of the graph in DOT format
- Return type: str
class pyagrum.MarkovBlanket(*args)
Section titled “class pyagrum.MarkovBlanket(*args)”Class building the Markov blanket of a node in a graph.
MarkovBlanket(m,n) -> MarkovBlanket : Parameters: : - m (pyagrum.DAGmodel) – a DAGmodel - n (int) – a node id
MarkovBlanket(m,name) -> MarkovBlanket : Parameters: : - m (pyagrum.DAGmodel) – a DAGmodel - name (str) – a node name
adjacencyMatrix()
Section titled “adjacencyMatrix()”adjacency matrix from a graph/graphical models
Compute the adjacency matrix of a pyAgrum’s graph or graphical models (more generally an object that has nodes, children/parents or neighbours methods)
- Returns: adjacency matrix (as numpy.ndarray) with nodeId as key.
- Return type: numpy.ndarray
arcs()
Section titled “arcs()”- Returns: the list of the arcs
- Return type: List
children(id)
Section titled “children(id)”- Parameters: id (int) – the id of the parent
- Returns: the set of all the children
- Return type: Set
connectedComponents()
Section titled “connectedComponents()”connected components from a graph/graphical models
Compute the connected components of a pyAgrum’s graph or graphical models (more generally an object that has nodes, children/parents or neighbours methods)
The firstly visited node for each component is called a ‘root’ and is used as a key for the component. This root has been arbitrarily chosen during the algorithm.
- Returns: dict of connected components (as set of nodeIds (int)) with a nodeId (root) of each component as key.
- Return type: dict(int,Set[int])
- Returns: a copy of the DAG
- Return type: pyagrum.DAG
hasSameStructure(other)
Section titled “hasSameStructure(other)”- Parameters: pyagrum.DAGmodel – a direct acyclic model
- Returns: True if all the named node are the same and all the named arcs are the same
- Return type: bool
nodes()
Section titled “nodes()”- Returns: the set of ids
- Return type: set
parents(id)
Section titled “parents(id)”- Parameters:
id (
int) – The id of the child node - Returns: the set of the parents ids.
- Return type: Set
size()
Section titled “size()”- Returns: the number of nodes in the graph
- Return type: int
sizeArcs()
Section titled “sizeArcs()”- Returns: the number of arcs in the graph
- Return type: int
sizeNodes()
Section titled “sizeNodes()”- Returns: the number of nodes in the graph
- Return type: int
toDot()
Section titled “toDot()”- Returns: a friendly display of the graph in DOT format
- Return type: str
